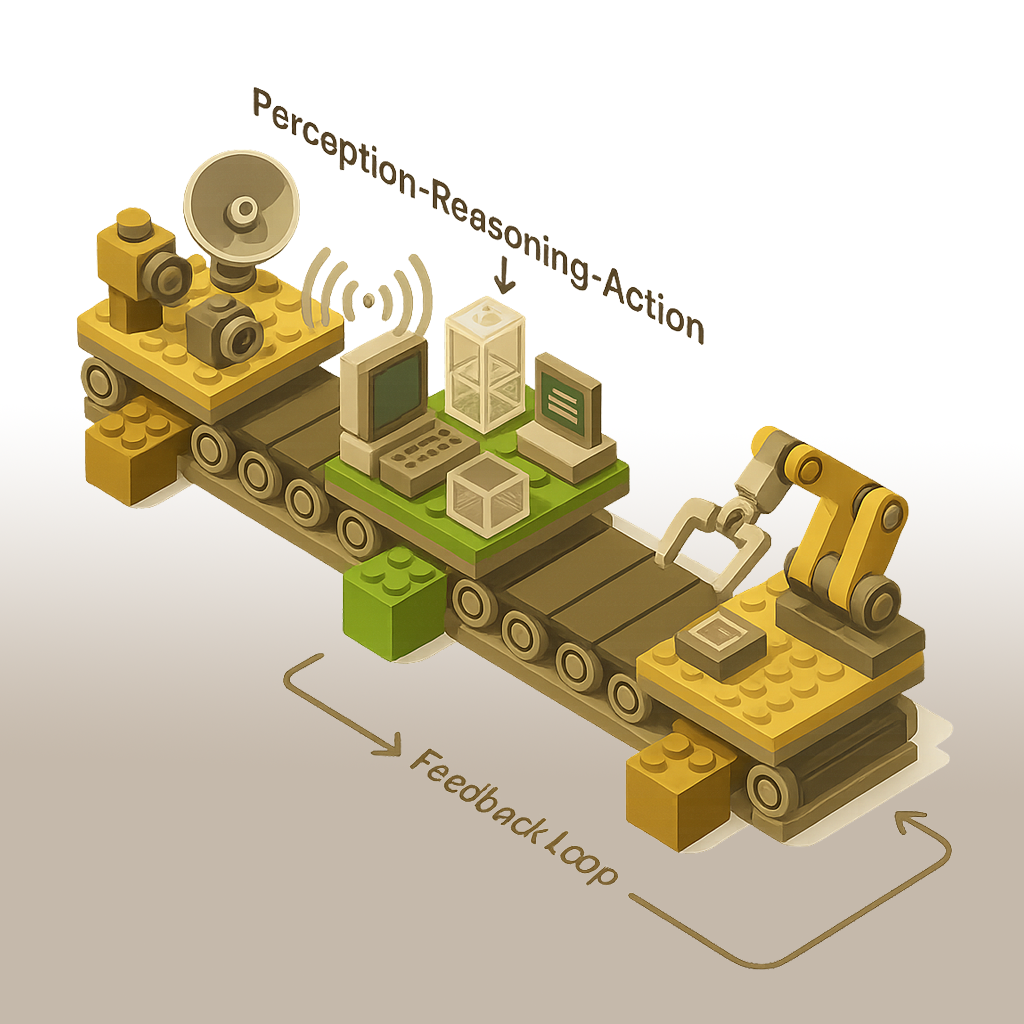
Perception-Reasoning-Action Loop Pattern
Complete Cognitive Systems for Enterprise AI
A comprehensive cognitive architecture that mirrors human information processing, enabling AI agents to perceive environments, reason about information, take actions, and learn from outcomes.
Create autonomous AI systems capable of sophisticated environmental interaction, abstract reasoning, and continuous improvement through feedback-driven cognitive cycles.
Pattern Overview
The Perception-Reasoning-Action (PRA) Loop implements a comprehensive cognitive architecture for AI agents that mirrors the fundamental information processing cycle found in human cognition. This pattern creates complete agent systems capable of perceiving their environment, reasoning about information, taking appropriate actions, and learning from outcomes.
The core principle lies in creating a continuous feedback loop where environmental inputs are transformed into structured representations, analyzed through reasoning processes, translated into appropriate actions, and refined through outcome evaluation. This creates a complete cognitive cycle that enables sophisticated interaction with complex environments.
Key Components
- Perception System: Multi-modal input processing and representation
- Reasoning Engine: Analytical processes for understanding and decision-making
- Action Framework: Execution capabilities for implementing decisions
- Feedback Mechanism: Outcome evaluation and learning processes
- Memory System: Storage and retrieval of experience and knowledge
End-to-End Processing from Input to Action and Feedback
The Perception-Reasoning-Action Loop's distinctive power comes from its implementation of complete cognitive cycles that transform raw input into meaningful action through structured information processing stages.
- Comprehensive Processing: Complete handling from initial perception to final action
- Continuous Improvement: Closed-loop learning from action outcomes
- Environmental Awareness: Sophisticated understanding of complex business contexts
- Autonomous Operation: End-to-end capabilities for independent task completion
Technical Architecture
System Components
1. Perception System
- • Multi-modal input processing (text, image, structured data)
- • Signal processing and feature extraction
- • Entity recognition and relationship mapping
- • Attention mechanisms for relevance filtering
2. Reasoning Engine
- • Knowledge integration from multiple sources
- • Inference mechanisms for drawing conclusions
- • Causal analysis for understanding relationships
- • Goal management and planning capabilities
3. Action Framework
- • Action selection from available options
- • Execution planning and sequencing
- • Tool and API integration for capability extension
- • Error detection and recovery mechanisms
Implementation Stack
Infrastructure
Heterogeneous compute appropriate to different components
Development Framework
Integrated environment for cognitive system implementation
Monitoring
Comprehensive visibility across the complete processing loop
Google Cloud Components
- • Document AI for perception of unstructured documents
- • Vision AI for image understanding
- • Natural Language API for text processing
- • Vertex AI for reasoning components
- • Cloud Functions for action execution
- • Workflows for process orchestration
Industry Applications
BFSI
- • Automated underwriting
- • Fraud investigation
- • Customer service automation
- • Trading systems
Manufacturing
- • Quality control
- • Process optimization
- • Supply chain management
- • Predictive maintenance
Healthcare
- • Clinical decision support
- • Care coordination
- • Medical imaging analysis
- • Patient monitoring
Retail/eCommerce
- • Personalized marketing
- • Inventory management
- • Price optimization
- • Customer service automation
Advantages & Limitations
Key Benefits
- Complete Processing: End-to-end capability from input to action
- Autonomous Operation: Self-contained systems for independent task execution
- Continuous Improvement: Learning from experience through feedback integration
- Environmental Adaptation: Adjusting to changing conditions through perception
- Comprehensive Intelligence: Integration of multiple cognitive capabilities
Challenges & Mitigations
Complexity Management
Modular implementation with clear interfaces
Error Propagation
Robust validation between processing stages
Performance Bottlenecks
Optimized information flow and parallel processing
Debugging Difficulty
Comprehensive logging and observability
Implementation Roadmap
Phase 1: Foundation
1-2 months
- • Establish core loop architecture
- • Implement initial perception capabilities
- • Develop basic reasoning processes
- • Create action frameworks
Phase 2: Initial Implementation
2-3 months
- • Deploy first complete loops
- • Implement feedback collection
- • Develop monitoring infrastructure
- • Begin learning mechanisms
Phase 3: Expansion
3+ months
- • Extend to additional domains
- • Enhance perception capabilities
- • Implement advanced reasoning
- • Expand action capabilities
Phase 4: Enterprise Scale
Ongoing
- • Establish comprehensive governance
- • Implement advanced analytics
- • Develop reusable patterns
- • Create enterprise knowledge integration