Agent Composability Pattern
Modular AI Systems at Enterprise Scale
A foundational architectural approach for building modular, extensible AI systems at enterprise scale through standardized interfaces and communication protocols.
Enable organizations to construct sophisticated AI solutions by assembling specialized agents into coordinated systems, each contributing distinct capabilities while operating within a unified framework.
Pattern Overview
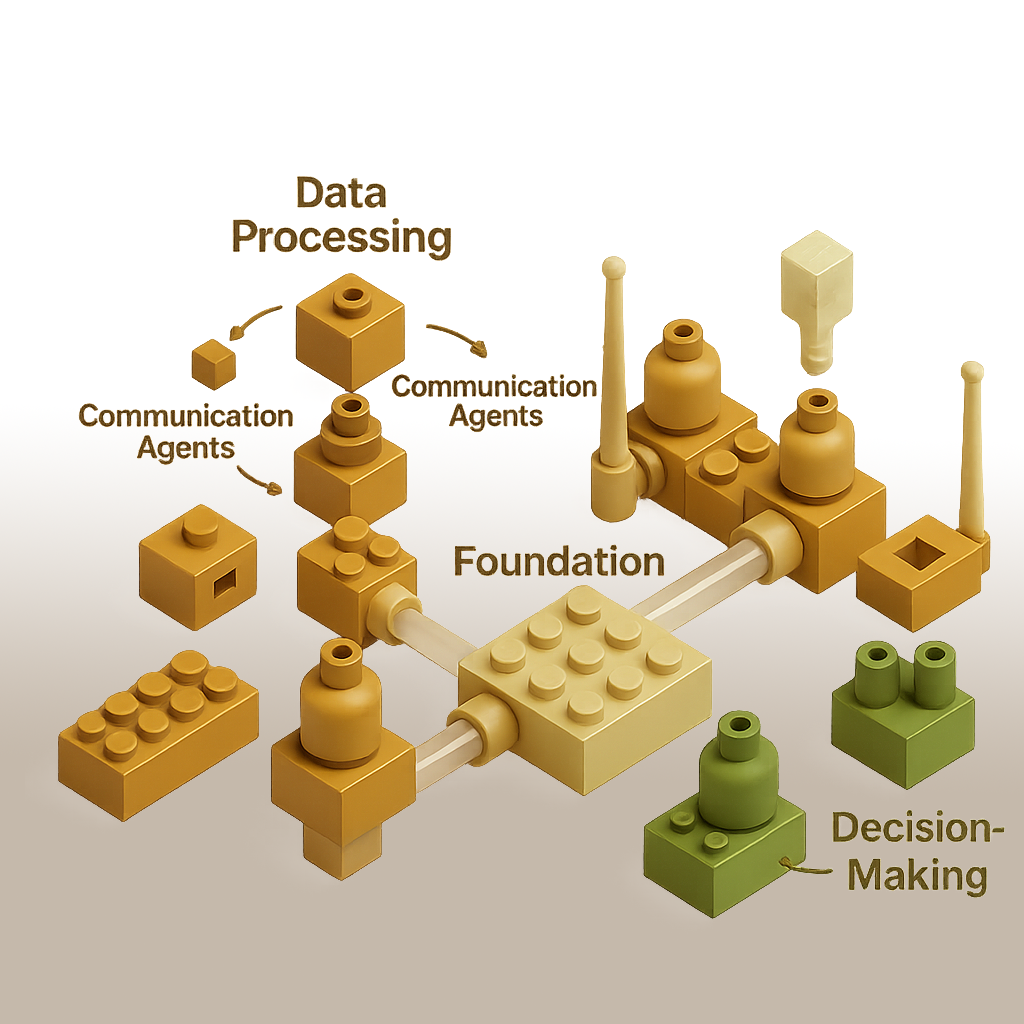
Agent Composability represents a foundational architectural approach for building modular, extensible AI systems at enterprise scale. This pattern enables organizations to construct sophisticated AI solutions by assembling specialized agents into coordinated systems, each contributing distinct capabilities while operating within a unified framework.
The core principle of Agent Composability lies in defining standardized interfaces and communication protocols that allow specialized AI components to be developed independently, tested rigorously, and combined flexibly. This modularity mirrors successful software engineering practices like microservices, bringing similar benefits to AI system design.
Key Components
- Agent Interface Definitions: Standardized contracts specifying inputs, outputs, and expected behaviors
- Coordination Mechanisms: Protocols governing agent communication and interaction
- State Management Systems: Mechanisms for maintaining consistent system state
- Service Discovery: Dynamic agent registration and capability advertisement
- Orchestration Layer: Component managing agent interactions and workflow
Standardized Interfaces
The Agent Composability Pattern's distinctive power comes from its ability to connect specialized AI components through well-defined interfaces, creating systems whose capabilities exceed the sum of their parts.
- Targeted Optimization: Each agent fine-tuned for its specific domain
- Independent Development: Teams can work in parallel on different agents
- Flexible Reconfiguration: Agents can be swapped without system-wide changes
- Incremental Enhancement: New capabilities via new agents
Technical Architecture
System Components
1. Agent Registry
- • Maintains catalog of available agents and capabilities
- • Handles registration, discovery, and metadata management
- • Implements versioning for multiple agent implementations
2. Interface Definition Framework
- • Standardizes input/output schemas and protocols
- • Defines error handling and exception patterns
- • Establishes performance contracts and SLAs
3. Communication Bus
- • Facilitates agent-to-agent communication
- • Implements sync and async messaging patterns
- • Provides reliable message delivery with retry logic
Implementation Stack
Infrastructure
Containerized deployment environment (Kubernetes) with service mesh for communication
Development Framework
Agent Development Kit (ADK) with interface contract enforcement
Monitoring
Distributed tracing for cross-agent workflows with OpenTelemetry instrumentation
Google Cloud Components
- • Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
- • Pub/Sub for event-driven communication
- • Cloud Run for serverless execution
- • Vertex AI for model serving
Industry Applications
BFSI
- • Risk assessment workflows
- • Customer onboarding automation
- • Financial advisory systems
Manufacturing
- • Quality control systems
- • Predictive maintenance
- • Supply chain optimization
Healthcare
- • Diagnostic support systems
- • Treatment planning
- • Patient monitoring
Retail/eCommerce
- • Personalized shopping
- • Omnichannel support
- • Inventory optimization
Advantages & Limitations
Key Benefits
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Easy reconfiguration for different use cases without rebuilding entire systems
- Specialized Expertise: Each agent can implement optimal approaches for its specific domain
- Scalability: Independent scaling of components based on workload demands
- Maintainability: Isolated components can be updated independently
- Reusability: Agents can be reused across multiple solutions and business domains
Challenges & Mitigations
Communication Overhead
Optimize message payloads and implement efficient protocols
Consistency Management
Implement distributed state management with transaction support
Interface Evolution
Versioning strategy with backward compatibility requirements
Testing Complexity
Component-level and integration testing frameworks
Implementation Roadmap
Phase 1: Foundation
1-2 months
- • Establish technology stack
- • Implement core infrastructure
- • Develop interface contracts
Phase 2: Initial Implementation
2-3 months
- • Develop first specialized agents
- • Build simple composite workflows
- • Implement monitoring
Phase 3: Expansion
3+ months
- • Add additional agents
- • Develop complex workflows
- • Optimize performance
Phase 4: Enterprise Scale
Ongoing
- • Advanced security
- • Establish MLOps practices
- • Develop reusable patterns