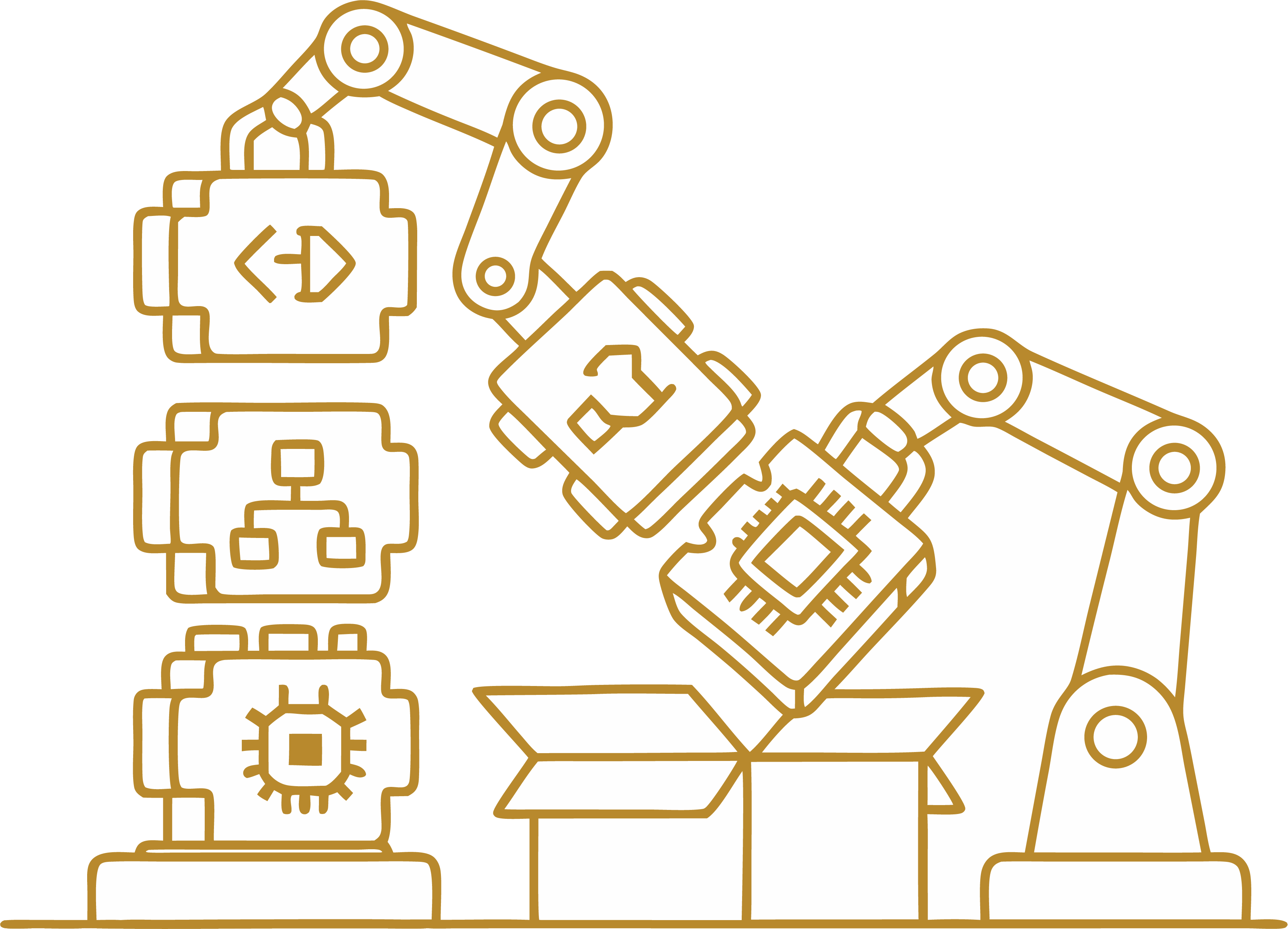
SquareShift's Layered Agent Operating Model
A comprehensive architectural framework for building enterprise-grade AI agents with core intelligence, modular adapters, and cross-cutting concerns for scalable, maintainable, and responsible AI systems.

Core Intelligence
The central hexagon represents the core intelligence of the AI agent, consisting of three fundamental layers that work together to provide strategic thinking, memory management, and reasoning capabilities.
Strategy Layer
- Task Planning: Decomposing complex objectives into actionable steps
- Goal Mapping: Aligning sub-tasks with overarching business objectives
- Meta-Goal Management: Managing hierarchical goal structures and dependencies
- Resource Allocation: Optimizing computational and temporal resources
- Priority Management: Dynamic task prioritization based on context
Memory Layer
- Context Retention: Maintaining conversation and task context across sessions
- Knowledge Storage: Persistent storage of learned information and experiences
- Embedding Management: Vector representations for semantic understanding
- Long-Term Storage: Hierarchical memory systems for knowledge persistence
- Memory Retrieval: Efficient access to relevant historical information

Reasoning Layer
- Multi-Step Logic: Complex reasoning chains and logical inference
- Chain of Thought (CoT): Transparent reasoning process documentation
- Tree of Thoughts (ToT): Parallel reasoning path exploration
- Uncertainty Quantification: Confidence estimation and risk assessment
- Causal Reasoning: Understanding cause-effect relationships
Adapters
The hexagonal adapters provide modular interfaces for the AI agent to interact with the external world. Each adapter is designed for specific capabilities while maintaining loose coupling with the core intelligence.
Perception
- Multimodal Understanding: Processing text, images, audio, and video
- Natural Language Processing: Text comprehension and generation
- Computer Vision: Image and video analysis
- Contextual Awareness: Environmental and situational understanding
- Sensor Integration: Real-time data ingestion from various sources
Tool Execution
- MCP (Model Context Protocol): Standardized tool and resource integration
- API Integration: RESTful and GraphQL service connections
- Function Calling: Dynamic tool selection and execution
- Database Operations: CRUD operations across data sources
- Workflow Orchestration: Multi-step process coordination
Learning
- Feedback Processing: Human and system feedback integration
- Reinforcement Learning: Behavior optimization through rewards
- Fine-tuning: Model adaptation to specific domains
- Preference Learning: User preference incorporation
- Continuous Improvement: Performance enhancement over time

Interaction
- Conversational Interfaces: Natural dialogue management
- User Experience: Intuitive interaction design
- Multi-channel Support: Web, mobile, voice, and chat interfaces
- Real-time Communication: Synchronous and asynchronous messaging
- Personalization: Context-aware user experiences
Deployment
- Infrastructure Management: Cloud and on-premise deployment
- Serving Systems: High-availability model serving
- Containerization: Docker and Kubernetes orchestration
- Resource Management: Auto-scaling and load balancing
- CI/CD Integration: Automated deployment pipelines

Observability
- Performance Monitoring: Real-time system health tracking
- Metrics Collection: Comprehensive telemetry and KPIs
- Distributed Tracing: End-to-end request tracking
- Alerting Systems: Proactive issue detection
- Analytics Dashboard: Business and technical insights
Cross-Cutting Concerns
These foundational concerns span across all components of the architecture, ensuring responsible, secure, and business-aligned AI agent operations at every level.
 Security
Security

- Input Validation: Comprehensive data sanitization and validation
- Safety Mechanisms: Preventing harmful or unintended behavior
- Attack Prevention: Protection against adversarial inputs and attacks
- Authentication: Secure user and system verification
- Data Protection: Encryption and privacy preservation
 Ethics
Ethics

- Value Alignment: Ensuring AI actions align with human values
- Bias Mitigation: Identifying and reducing algorithmic bias
- Fairness: Equitable treatment across user groups
- Impact Assessment: Evaluating societal and individual impacts
- Responsible AI: Ethical development and deployment practices
 Business Value
Business Value

- ROI Alignment: Ensuring positive return on investment
- Use Case Optimization: Maximizing value for specific applications
- Cost Management: Efficient resource utilization
- Business Metrics: Tracking value delivery and impact
- Strategic Integration: Alignment with business objectives
 Ecosystem
Ecosystem

- Integration Standards: API and protocol standardization
- Plugin Architecture: Extensible and modular design
- Third-party Compatibility: Seamless external system integration
- Interoperability: Cross-platform and cross-vendor support
- Ecosystem Growth: Fostering community and partnerships
 Governance
Governance

- Audit Systems: Comprehensive activity logging and review
- Compliance: Regulatory and industry standard adherence
- Policy Enforcement: Automated policy compliance checking
- Oversight Mechanisms: Human oversight and intervention capabilities
- Risk Management: Proactive risk identification and mitigation
 User Trust
User Trust

- Explainability: Clear reasoning and decision explanation
- Predictability: Consistent and reliable behavior
- Transparency: Open communication about capabilities and limitations
- User Control: Meaningful human agency and oversight
- Trust Building: Continuous relationship building with users
Why the Layered Agent Operating Model?
Architectural Benefits
-
 Modularity & Flexibility: Clear separation of concerns enables independent development and testing of components
Modularity & Flexibility: Clear separation of concerns enables independent development and testing of components -
 Pluggable Adapters: Easy integration of new capabilities without modifying core intelligence
Pluggable Adapters: Easy integration of new capabilities without modifying core intelligence -
 Testability: Independent testing of adapters and core components through clear interfaces
Testability: Independent testing of adapters and core components through clear interfaces -
 Scalability: Horizontal scaling of individual adapters based on demand
Scalability: Horizontal scaling of individual adapters based on demand
Business Impact
-
 Faster Time-to-Market: Parallel development of adapters accelerates delivery
Faster Time-to-Market: Parallel development of adapters accelerates delivery -
 Reduced Maintenance: Isolated components minimize impact of changes and updates
Reduced Maintenance: Isolated components minimize impact of changes and updates -
 Future-Proof Design: Architecture adapts to changing requirements and technologies
Future-Proof Design: Architecture adapts to changing requirements and technologies -
 Risk Mitigation: Comprehensive cross-cutting concerns ensure responsible AI deployment
Risk Mitigation: Comprehensive cross-cutting concerns ensure responsible AI deployment
Ready to Implement SquareShift's Layered Agent Operating Model?
Partner with SquareShift to design and implement enterprise-grade AI agents using our proven Layered Agent Operating Model framework.